Ever wondered why some apps feel so incredibly fast and smooth? There’s a good chance you’re experiencing the power of React, a popular toolkit for building modern user interfaces. Think of it as a set of digital LEGO® bricks that help create amazing online experiences, piece by reusable piece.
But what is React actually used for, and why do so many developers love it? In this guide, we’ll answer just that. We’ll cover its key features, look at real-world examples, and even explore how it can bring a new level of power to your WordPress site. Let’s see!

Get matched with the developer
that is perfect fit for your WordPress or WooCommerce needs.
Start a project
How React works: An overview
At its core, React is a free frontend JavaScript library created by Meta (Facebook) for building user interfaces (UIs). It is a powerful and flexible toolkit for crafting the frontend of the website, i.e., the parts of a website or app that users see and interact with.
As you’d expect, it powers platforms like Facebook and Instagram, but it’s also the tech behind Airbnb, Netflix, and Instacart. Here are some of the reactive, dynamic capabilities it adds to Airbnb’s website, for example:
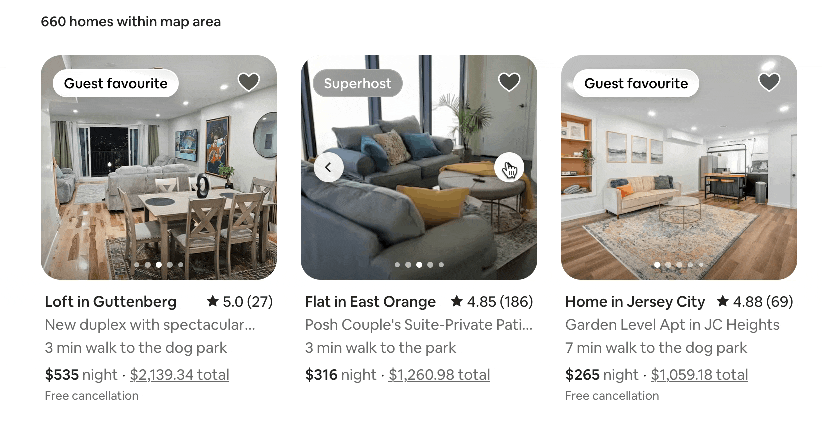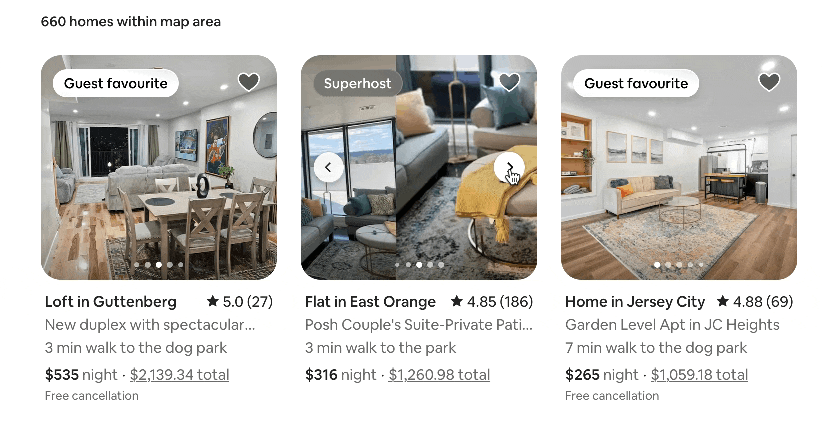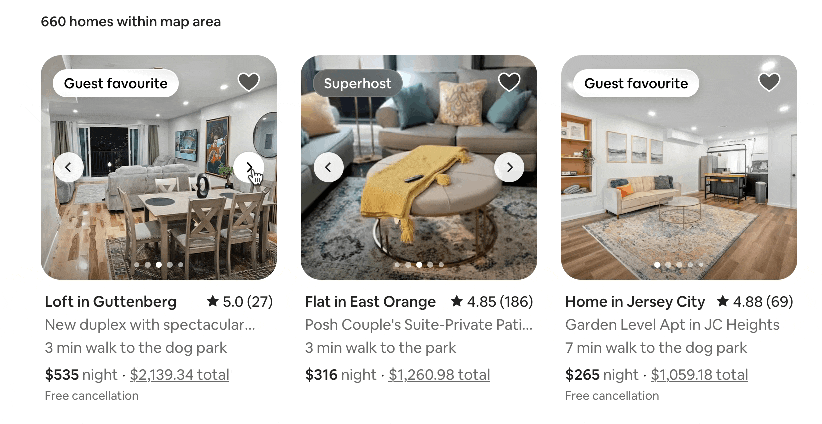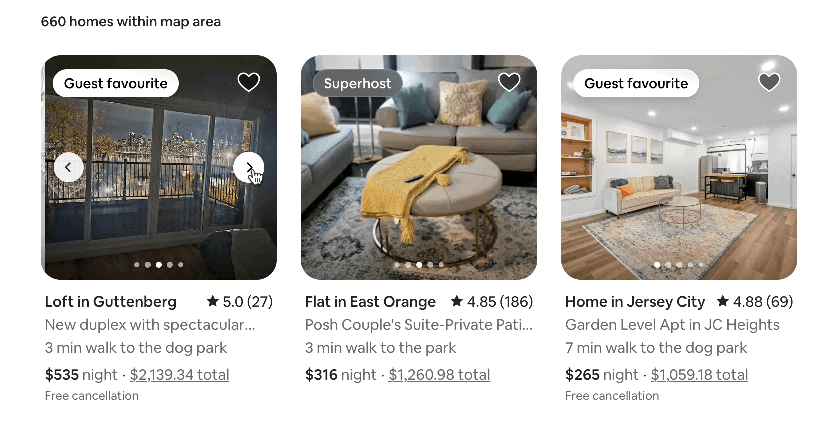
But how does it turn code into the fast, dynamic experiences we love? It all comes down to a few brilliant core concepts.
Components: The building blocks
At the very heart of React is the idea of components. These are independent, reusable elements you can use to design your user interface. Each component manages its own logic and appearance.
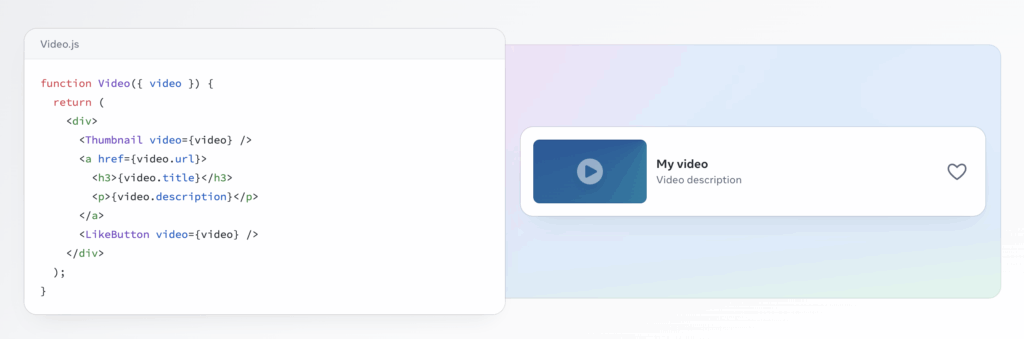
For example, imagine a social media page. You could have separate components for:
- A navigation bar at the top.
- A “Create Post” box.
- An individual post in the feed.
- A “Like” button inside that post.
- A comment section.
The beauty of this approach is that you can build a component once (like the “Like” button) and reuse it in many different places. If you need to update it, you only have to change it in one spot, and it will update everywhere it’s used. This keeps your code organized, clean, and much easier to manage.
Declarative UI: Tell React what you want
React uses a declarative approach to building UIs. This might sound technical, but the idea is simple. You just declare what you want the screen to look like for any given piece of data, and React handles the rest.
It’s like ordering a coffee.
- A declarative request is “I’d like a large latte with oat milk.” You describe the final result you want.
- An imperative request would be “Grab a large cup, steam the oat milk to 65 degrees, pull a double shot of espresso, pour the milk into the espresso, and put a lid on it.” You give step-by-step instructions.
With React, you simply tell it, “When the data says the user is logged in, show their profile picture.” You don’t have to write the step-by-step instructions for removing the ‘Login’ button and adding the picture. This makes your code more predictable and easier to debug.
Virtual DOM: The secret to speed
One of React’s most famous features is the Virtual DOM, which is key to its impressive speed. The DOM (Document Object Model) is the browser’s programming interface for a web page; it’s a tree-like structure of all the elements on the page. Directly changing the real DOM is slow and can make UIs feel clunky.
React gets around this with a clever trick.
- It creates a copy: React keeps a lightweight copy of the real DOM in memory, called the Virtual DOM.
- It updates the copy first: When something changes in your app (like you clicking a “Like” button), React updates this Virtual DOM first, which is incredibly fast.
- It compares the two: React then compares the updated Virtual DOM with the version from before the change. This comparison process is called “diffing.”
- It makes smart updates: It figures out the absolute minimum number of changes needed to make the real DOM match the new Virtual DOM. Then, it performs that one specific, surgical update instead of reloading the whole page or larger parts of it.
This process minimizes slow interactions with the real DOM, resulting in the snappy, responsive user experience that React is famous for.
JSX: Writing UI in your JavaScript
Finally, React developers typically use JSX (JavaScript XML). JSX is a special syntax that lets you write what looks like HTML directly inside your JavaScript code. While it might look strange at first, it’s an excellent idea.
For example, a simple JSX element might look like this:
const greeting = <h1>Hello, Codeable reader!</h1>;Even though it looks like HTML, it’s actually JavaScript. Before the code runs in the browser, a tool called a transpiler converts this JSX into regular JavaScript that browsers can understand.
This allows you to keep the structure of your UI (the HTML-like part) and the logic that controls it (the JavaScript part) together in one place – inside the component. It makes your code incredibly readable and easier to visualize what your component will look like when it appears on the screen.
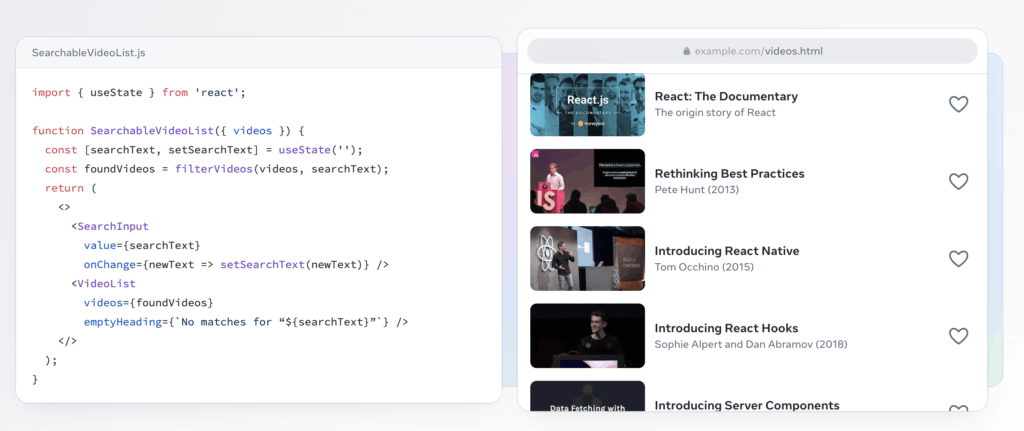
How React works in practice
So, we know React uses components, a Virtual DOM, and JSX. But how do these pieces fit together in a real project? Let’s walk through the day-to-day workflow of how an idea becomes an interactive element on the screen.
Defining a component
First, a developer defines a component. In modern React, this is usually just a simple JavaScript function. This function’s job is to describe and return the UI for that specific piece of the page using JSX. Think of the function as a recipe, and the JSX it returns is the description of the finished dish.
Using state and props
Components aren’t static; they need to handle data. They do this using two important concepts: props and state. Understanding the difference is key to understanding React.
- Props (short for properties): These are used to pass data down from a parent component to a child component. Props are read-only, meaning the child component can’t change them. Think of it like a car’s make and model. The factory (parent component) assigns it the make=”Tesla” and model=”Model Y” props. The car itself (child component) can’t change those fundamental properties. They are used for configuration.
- State: This is data that is managed inside a component and is expected to change over time. When a component’s state changes, React automatically re-renders the component to reflect the new information. To use our car analogy, the state could be its current speed or whether the lights are on. The car itself controls these things based on interactions (like pressing the accelerator).
So, props are for passing data in, while state is for managing data that changes inside a component.
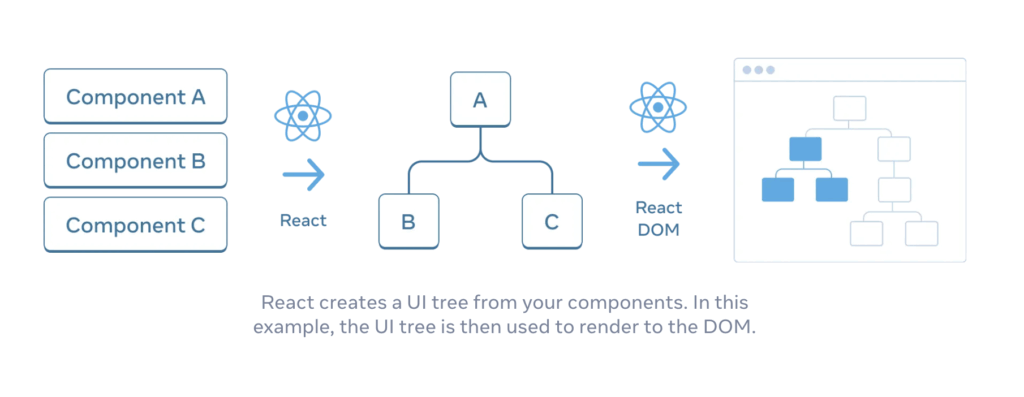
Building a component tree
A React application is basically one giant component tree. It starts with a single root component (often called App), which renders other components. Those components, in turn, can render even more components. All data (props) can be passed down through the components, creating a clear and organized data flow.
Triggering updates with reconciliation
Let’s say you click a button that “likes” a photo.
- That click event would call a function that updates the component’s state (e.g., changing isLiked from false to true).
- React detects this state change and triggers a re-render.
- Instead of touching the slow, real DOM, React’s reconciliation process (also known as the “diffing algorithm”) kicks in. It quickly builds a new Virtual DOM tree that reflects the change.
- It compares this new tree to the previous one and identifies the one tiny difference: the “Like” button’s appearance needs to change.
- Finally, React performs an efficient update, telling the real DOM to only alter that single button. It doesn’t touch anything else on the page.
This entire cycle, from state change to a minimal, targeted update, happens in a flash, making the application feel instantaneous and highly responsive.
Main scenarios where React is the best choice
React is a versatile library, but its core strengths make it an absolute powerhouse in certain situations. It’s not just about what you can build with React, but where it truly makes development faster, smarter, and more scalable.
Here are the main scenarios where developers and businesses confidently turn to React.
Single-page applications (SPAs)
Think about using an app like Gmail or Trello. You click around, open emails, and move cards, but the page never does a full, jarring reload. That’s a Single-Page Application. These apps load one single HTML page and then dynamically update the content as you go, providing a fluid, desktop-like experience.
You can see this in action when browsing through React’s docs:
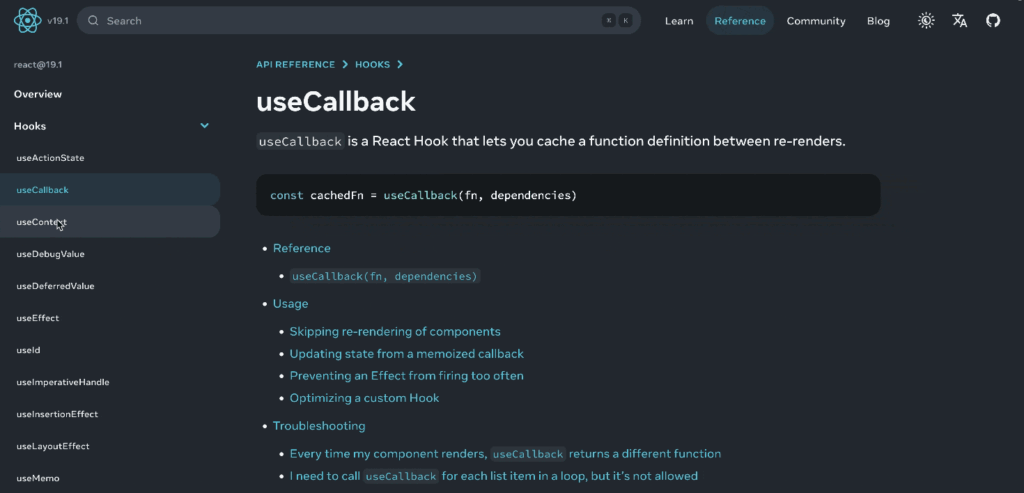
- Why React is perfect for this: Its Virtual DOM and super-efficient update process are tailor-made for SPAs. It ensures that transitions are smooth and seamless, making the application feel incredibly fast and responsive.
- Great for building: Modern web apps like Facebook, project management tools like Asana, and countless Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platforms.
Complex and interactive user interfaces
When your app involves a lot of user interaction, real-time updates, and complex screens, React is a lifesaver. Think of dashboards with constantly changing graphs, or online design tools with countless moving parts.
- Why React is perfect for this: Its component-based architecture lets you break down even the most complicated UI into small, manageable, and independent pieces. This makes both building and fixing complex interfaces much easier.
- Great for building: Live data dashboards, chat applications, interactive data visualization tools like Figma, and complex online forms.
Cross-platform mobile apps (with React Native)
What if you could build one app that works on both iOS and Android phones, using the same technology you use for the web? That’s the promise of React Native, a sister framework to React.js. It lets you use the same React principles to build truly native mobile apps.
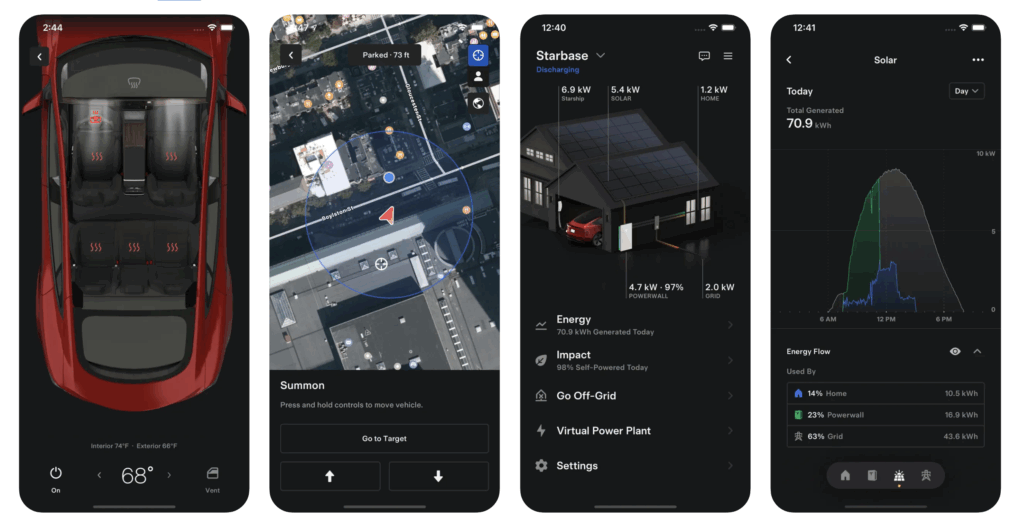
- Why React is perfect for this: It allows you to write your code once and deploy it on two different platforms. This drastically cuts down on development time and cost compared to building two separate apps from scratch.
- Great for building: Many of the apps you use daily, including Instagram, Shopify, Discord, and Pinterest.
Reusable UI components and design systems
For large organizations, maintaining a consistent brand and user experience across all digital products is crucial. React’s component model is the ideal foundation for building a centralized library of UI elements, often called a design system.
- Why React is perfect for this: You can create a master set of standardized components, such as buttons, dropdowns, form fields, that can be shared across an entire company. This ensures consistency and speeds up development for any new project.
- Great for building: Enterprise-level applications and product suites where a consistent look and feel is non-negotiable.
Apps with real-time data updates
If your application needs to display data that changes by the second, you need a library that can keep up without slowing the user’s browser to a crawl.
- Why React is perfect for this: Its ability to efficiently re-render only the tiny parts of the UI that have changed makes it perfect for live data. The rest of the page remains untouched and stable.
- Great for building: Financial trading platforms with live stock tickers, sports betting apps with real-time scores, and social media news feeds.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs)
PWAs are web applications that deliver a native app-like experience. They can work offline, send push notifications, and be added to your phone’s home screen, all without visiting an app store.
- Why React is perfect for this: React’s performance optimizations and component structure align perfectly with the goals of a PWA, helping to create a fast, reliable, and engaging experience for users on any device.
- Great for building: Mobile-first experiences for brands like Pinterest and Starbucks, which use PWAs to reach a wider audience.
SEO-friendly sites with server-side rendering (SSR)
Traditionally, SPAs could sometimes be tricky for search engines like Google to “read,” which could hurt SEO. React, when paired with frameworks like Next.js, can solve this with Server-Side Rendering. This means the initial page is fully formed on the server before being sent to the user.
- Why React is perfect for this: It gives the user a fast initial page load and provides search engines with a fully-rendered HTML page to crawl, boosting SEO performance.
- Great for building: E-commerce sites like Walmart, content-heavy blogs, and news websites, where being found on Google is critical.
Large-scale applications with growing teams
As a project grows and more developers join the team, keeping the code clean and manageable can be a huge challenge.
- Why React is perfect for this: Its component-based structure, predictable data flow, and massive community support help enforce good habits. It makes it easier to maintain a consistent codebase and get new team members up to speed quickly.
- Great for building: The complex applications that power companies like Netflix, PayPal, and Uber.
As you can see, from snappy single-page apps to massive e-commerce platforms and the mobile apps in your pocket, React’s flexibility makes it a powerful ally. Its core principles of component-based design and a laser focus on performance are what make it the top choice for such a wide variety of digital experiences.
Build your React project with Codeable
It’s clear that React can transform a good idea into an exceptional digital experience. That’s one of the reasons why it is the most popular frontend framework. But turning that potential into a polished, high-performance application requires deep expertise. So, how do you bring your vision to life without the headaches of a complex development project?
That’s where Codeable comes in. Instead of spending months learning React or searching for talent, you can instantly connect with our elite, pre-vetted React developers. While we’re renowned for our WordPress mastery, our dev experts are also specialists in modern frameworks like React. Whether you’re building a new app from scratch or supercharging your existing site, we can provide the right talent for the job, guaranteed.
Don’t let technical hurdles hold you back. Post your project on Codeable today and get a free, no-obligation estimate from a vetted React expert.
 Dream It
Dream It