We need to say this right here at the start: Node.js and React aren’t competitors. In fact, they work together.
Node.js runs on the server (backend), handling data storage, user authentication, and API endpoints that send information to your application. React runs in the browser (frontend), building the user interface and managing what users see and interact with.
Both use JavaScript, which means you can use the same programming language for your entire web application. This eliminates the need to learn separate backend languages like Python or PHP alongside frontend JavaScript.
Development teams can share knowledge more easily, use similar tools and libraries, and developers can work on both parts of an application without switching mental contexts. The real question isn’t Node.js vs React, but how to use them together effectively.

Get matched with the developer
that is perfect fit for your WordPress or WooCommerce needs.
Start a project
Understanding Node.js: The backend powerhouse
Node.js is not a programming language or framework. Instead, it’s what’s called a runtime environment, and it’s meant to let you run JavaScript code on servers instead of just in web browsers. Think of it as the engine that powers your backend operations.
Core architecture
Node.js uses a single-threaded, event-driven model that handles multiple requests efficiently. What this means is that when a request comes in, Node.js processes it without blocking other requests.
For heavy operations like reading files or querying databases, it hands these tasks off to a background thread pool (managed by libuv) while continuing to handle other requests.
This makes Node.js extremely efficient for applications that involve lots of data input/output operations.
Key use cases
Node.js excels at building scalable REST APIs, real-time applications like chat systems or live updates, data streaming services, and microservices architectures. It’s particularly strong when your application needs to handle many concurrent connections or process data streams continuously.
Ecosystem
The Node.js ecosystem revolves around npm (Node Package Manager), which provides access to hundreds of thousands of reusable code packages. Popular frameworks include Express.js for building APIs quickly with minimal setup, Koa.js for a more modern, lightweight approach, and NestJS for larger applications that need structured, enterprise-level organization.
Understanding React: The user interface library
React, short for React.js, is a JavaScript library specifically designed for building user interfaces. It’s declarative, which means you describe what the UI should look like in different states, and React automatically handles updating the interface when data changes. You focus on the “what” rather than the “how.”
Core architecture
React uses a component-based structure where you build interfaces from small, reusable pieces called components. Each component manages its own logic and rendering.
React’s secret weapon is the Virtual DOM, a lightweight copy of the actual webpage structure kept in memory. When changes occur, React compares the new Virtual DOM with the previous version through a process called “reconciliation,” then efficiently updates only the parts of the real DOM that actually changed.
Here’s an illustration from the React docs where you can see this in action:
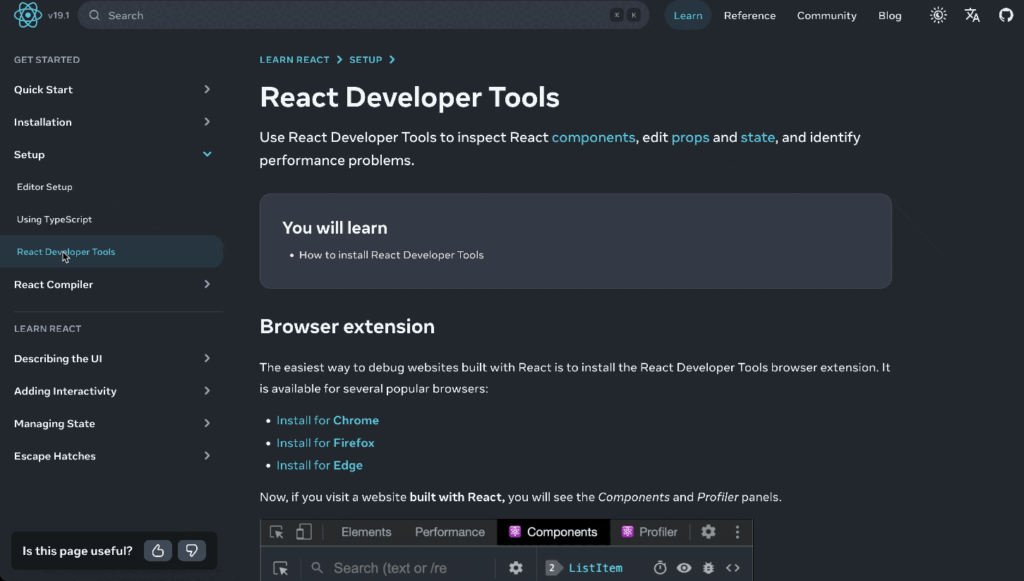
This makes React applications fast and responsive.
Key concepts
React relies on JSX, which allows you to write HTML-like syntax directly in your JavaScript code, making components easier to read and write.
Here’s an example of JSX syntax, also from the React docs, along with its output:
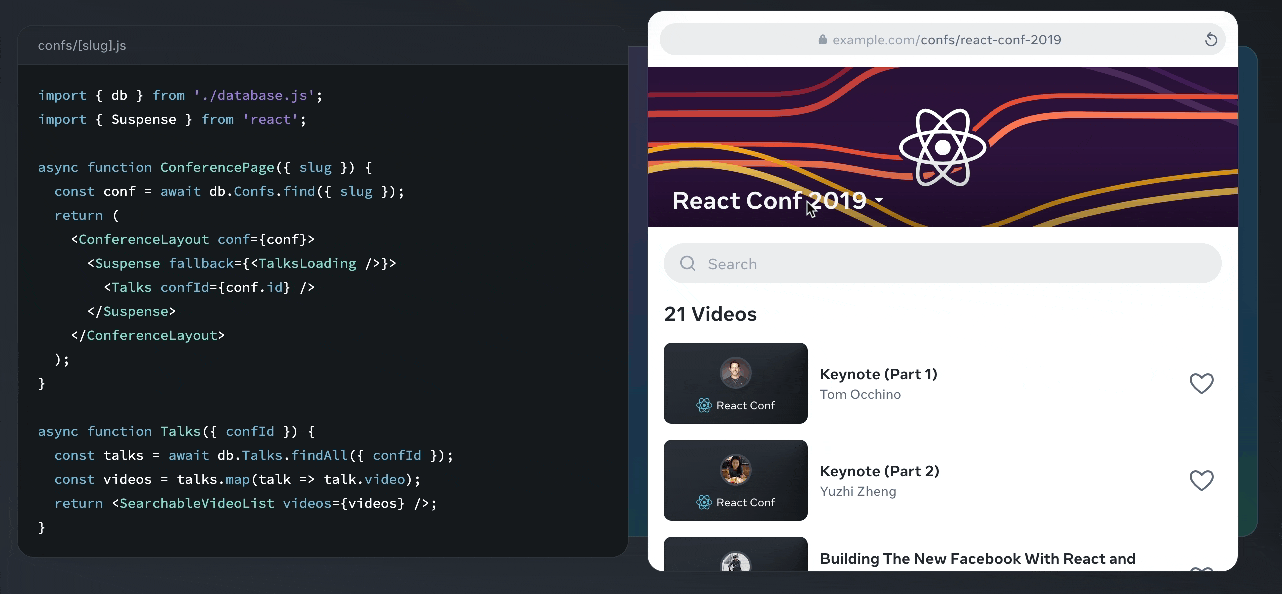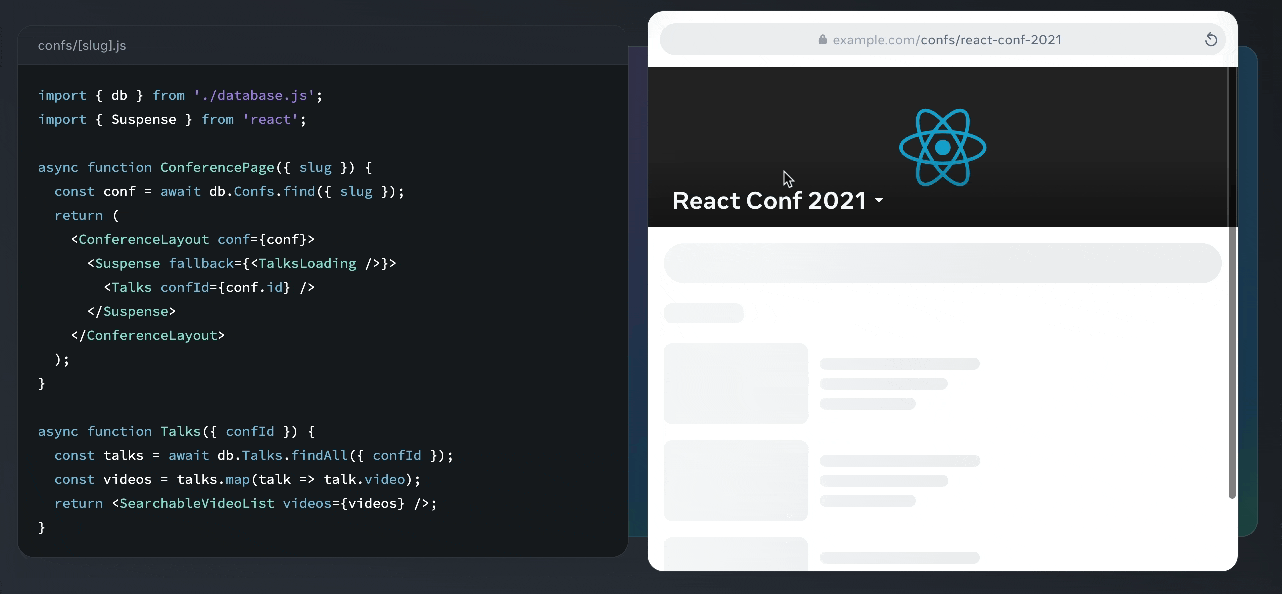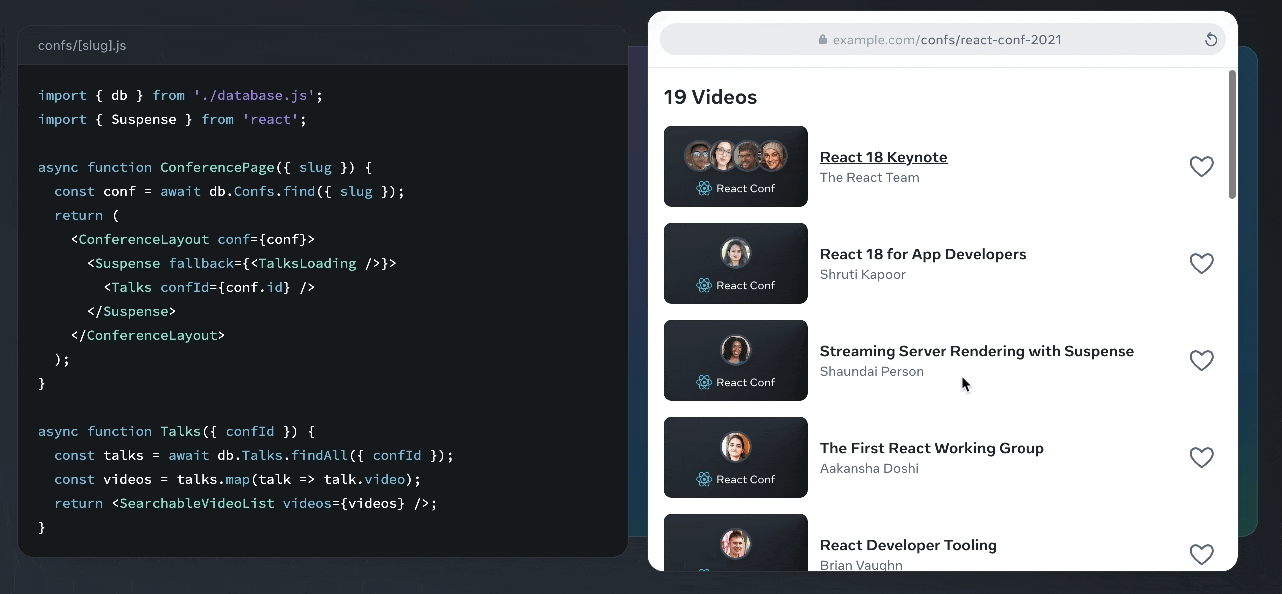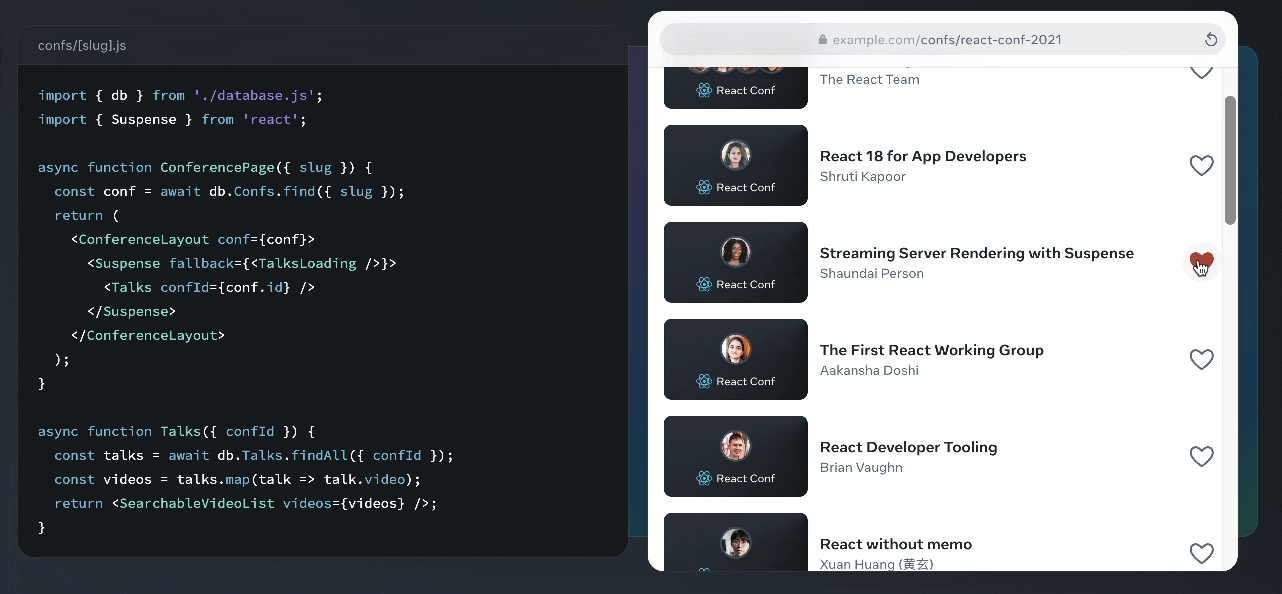
React follows a one-way data flow where information passes from parent components to child components through “props” (properties). This predictable pattern makes debugging easier and prevents common state management issues.
Ecosystem
React’s power expands significantly with additional libraries:
- React Router handles navigation in Single-Page Applications, allowing users to move between different views without full page reloads.
- Redux manages complex application states when data needs to be shared across many components.
- Modern React frameworks like Next.js build on React to provide server-side rendering, routing, and other production-ready features out of the box.
Deciding which technology to use: A strategic framework
The decision between focusing on Node.js or React depends on where your project’s complexity lies – on the backend (data processing, business logic) or the frontend (user interactions, interface complexity).
When to prioritize Node.js
Choose Node.js as your primary focus for backend-heavy projects where the user interface is simple or doesn’t exist at all.
This includes building APIs that serve mobile applications, creating microservices that handle specific business functions, processing IoT sensor data, or building command-line tools.
In these scenarios, most of your development effort goes into server-side logic, data handling, and system integration.
When to prioritize React
React is popular for frontend-heavy projects where user experience drives the application’s value, so that’s where you should prioritize it.
Examples include complex data visualization dashboards, interactive design tools, real-time collaboration platforms, or any application where users spend significant time interacting with sophisticated interfaces.
Here, the backend might be relatively simple – perhaps just a basic API – while the frontend requires complex state management and user interactions.
When you need both
Most modern web applications require both robust backend functionality and rich user interfaces.
For instance, eCommerce sites need payment processing, inventory management, and product catalogs (backend complexity) plus shopping carts, product filters, and checkout flows (frontend complexity). Social media platforms need user authentication, content storage, and recommendation algorithms (backend) plus feeds, messaging interfaces, and profile management (frontend).
Something like the MERN stack – MongoDB (database), Express.js (web framework), React.js (frontend), Node.js (runtime) – provides a complete JavaScript solution for full-stack development, allowing teams to use one language throughout their entire application.
Here’s a real-world workflow with the stack in your average eCommerce platform:
- User visits frontend, React renders product list UI.
- React fetches products from backend (Express/Node) via API request.
- Express/Node receives request, queries MongoDB for product data.
- MongoDB returns product data, Express/Node sends JSON to React.
- React displays products to the user.
- User adds item to cart in React state.
- User places order, React sends order details to Express/Node API.
- Express/Node validates order, saves it to MongoDB.
- MongoDB stores order and returns confirmation.
- Express/Node sends confirmation back to React.
- React shows order success message to the user.
Real-world adoption: Who uses them and why
From your news feed to your shopping cart, React and Node.js power some of the world’s most popular apps, platforms, and services:
- Facebook (Meta) actually created React to efficiently manage complex, fast-updating user interfaces. React drives features like the News Feed, Messenger, and other interactive elements. Node.js powers internal build tools, development servers, and certain service layers, supporting rapid development and deployment at scale.
- Netflix uses React for its web interface and some TV apps, enabling smooth, responsive browsing of movie catalogs and personalized recommendations. Node.js supports server-side rendering, API services, and performance optimization across devices.
- Airbnb uses React to deliver dynamic property listings, interactive booking flows, and responsive host management tools. Node.js handles backend tasks such as search, messaging, and booking coordination, enabling real-time marketplace functionality.
- Shopify uses React (including its Polaris component library) for merchant admin panels and customizable storefronts. Node.js supports API infrastructure, webhook processing, and integration with third-party apps.
Get your Node.js and React project off the ground with Codeable
Codeable is a freelancer platform that connects you with pre-vetted, highly experienced developers specializing in web development technologies, including Node.js and React.js. Many experts are proficient in full-stack development, capable of handling both the frontend and backend aspects of your project.
Codeable connects you with one to five ideal experts based on your specific requirements, saving you the time of sifting through thousands of applicants. You work with the matched experts in a shared space to define the scope, then hire your preferred developer at a fair, fixed price determined by an average of the expert estimates, not a race-to-the-bottom bid.
Payments are held in a secure escrow system and are only released when you mark the project as complete. All work is backed by a money-back guarantee, ensuring quality and commitment.
From small fixes to full-stack MERN applications, Codeable’s developers can provide tailored solutions. Submit your first project and experience the difference for yourself!

 Dream It
Dream It